Why Is My Dog Dragging Their Back Legs? Causes and Solutions
Dragging back legs can be distressing to both dogs and their owners. Understanding the causes and exploring effective solutions is critical for your pet’s comfort and quality of life.
On this page, we’ll explain why your dog may be dragging their back legs, the potential health conditions that could be responsible, and the steps you can take to address this issue.
Why Would a Dog Drag Their Back Legs?
Dogs drag their back legs for various reasons, ranging from temporary issues like muscle strain to more serious conditions such as nerve damage or spinal problems.
Observing your dog’s symptoms and behavior can help pinpoint the underlying cause and guide you in seeking appropriate veterinary care.
Common Causes of Back Leg Dragging in Dogs
1. Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD)
- What It Is: A spinal condition where the cushioning discs between vertebrae bulge or rupture, causing pain and nerve compression.
- Symptoms: Weakness, paralysis, pain when touched, reluctance to move, and dragging of back legs.
- Who Is Affected: Common in breeds like Dachshunds, French Bulldogs, and Beagles.
2. Degenerative Myelopathy
- What It Is: A progressive disease affecting the spinal cord in older dogs, leading to hind limb weakness and paralysis.
- Symptoms: Wobbling gait, scuffing hind paws, and gradual loss of mobility.
- Who Is Affected: Often seen in large breeds such as German Shepherds and Boxers.
3. Hip Dysplasia
- What It Is: A genetic condition where the hip joint fails to develop properly, leading to arthritis and mobility issues.
- Symptoms: Difficulty standing, stiffness, and dragging one or both back legs.
- Who Is Affected: Most common in large and giant breeds.
4. Neurological Disorders
- Examples:
- Spinal cord injuries from trauma or accidents.
- Tumors compressing nerves or the spine.
- Infections such as meningitis.
- Symptoms: Sudden or gradual loss of coordination, inability to move the back legs, and incontinence.
5. Arthritis
- What It Is: Inflammation of joints due to aging, wear and tear, or underlying diseases.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of canine arthritis include pain, stiffness, reduced mobility, and dragging feet while walking.
6. Other Possible Causes
- Tick Paralysis: Toxins released by ticks can temporarily paralyze the hind legs.
- Infections: Conditions such as Lyme disease can lead to joint and nerve inflammation.
- Muscle Injuries: Strains or sprains from overexertion may cause temporary weakness.
Steps to Diagnose the Cause
Proper diagnosis is essential for determining the cause and implementing the best solution. Here’s what you can expect during the diagnostic process:
Veterinary Examination
- Physical assessment of the spine, hips, and limbs.
- Neurological tests to evaluate reflexes and coordination.
Imaging Techniques
- X-Rays: To identify bone abnormalities or arthritis.
- MRI/CT Scans: For detailed views of the spinal cord and nerves.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood tests to rule out infections or systemic diseases.
- Tick-borne disease panels if exposure is suspected.
Electrodiagnostic Testing
- Measures nerve and muscle function to pinpoint neurological issues.
Treatment Options for Back Leg Dragging
1. Medications
- For Pain and Inflammation:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Corticosteroids for severe inflammation.
- For Nerve Disorders:
- Nerve-stimulating medications or supplements.
- Antibiotics:
- Used for infections such as Lyme disease.
2. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Hydrotherapy: Strengthens muscles with low joint impact.
- Laser Therapy: Reduces inflammation and stimulates nerve function.
- Massage and Stretching: Relieves tension and promotes circulation.
3. Surgery
- Recommended for conditions such as severe IVDD or spinal injuries where conservative treatments fail. Success depends on the severity and timing of intervention.
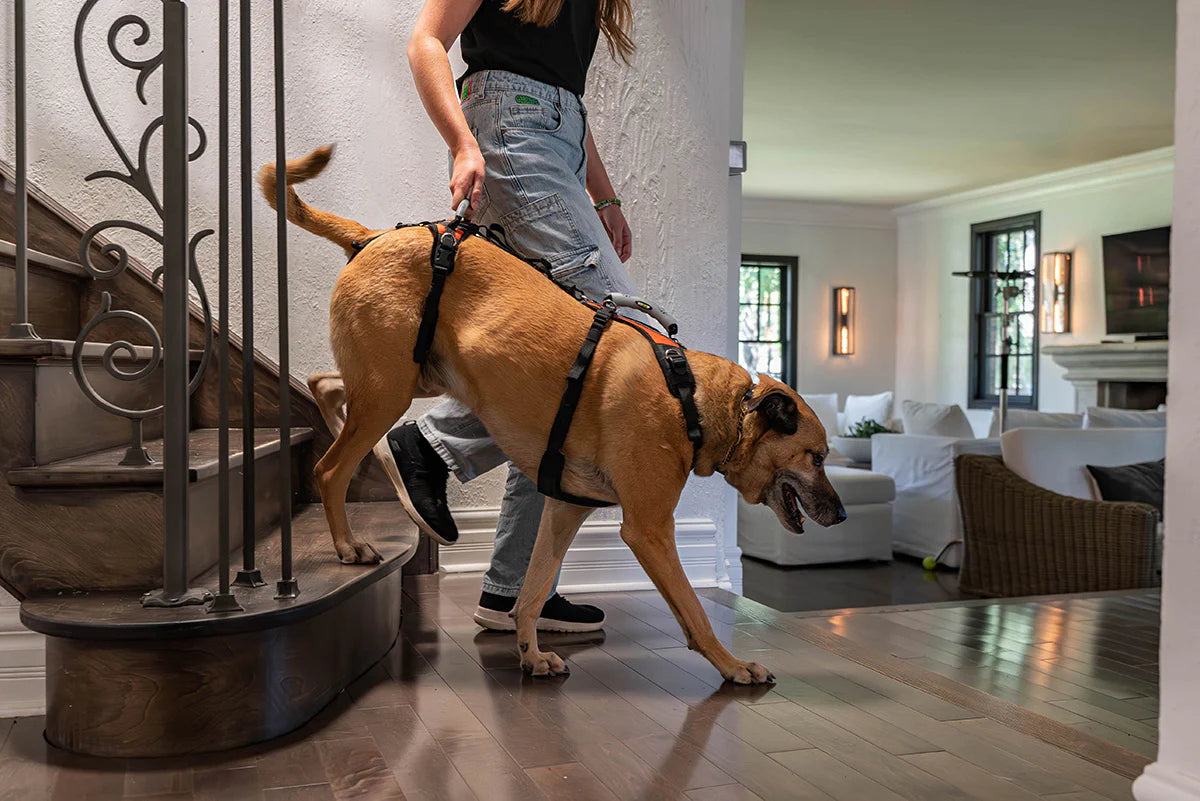
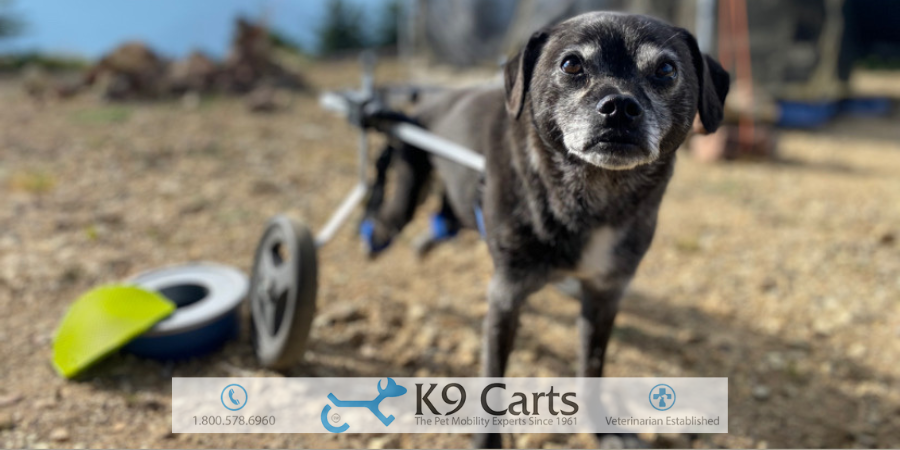
4. Custom-Built Dog Wheelchairs
- For dogs with permanent mobility loss or severe hind-limb weakness, a canine wheelchair can restore independence.
- Why Choose Custom Options:
- Tailored to your dog’s size, weight, and condition.
- Supports rehabilitation while improving mobility and quality of life.
- At K9 Carts, our custom-built wheelchairs are designed by experts, ensuring your dog’s comfort and functionality.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Weight Management: Reduces strain on joints and the spine.
- Home Modifications:
- Adding ramps and non-slip mats for easier movement.
- Limiting stairs to prevent further injury.
When to Consider a Dog Wheelchair
If your dog is unable to regain full mobility despite treatment, a wheelchair can provide much-needed support. Here’s when to explore this option:
- Your dog is experiencing permanent paralysis or severe weakness in the hind legs.
- Rehabilitation is ongoing, but your dog needs additional mobility support.
- Your dog’s mental health and happiness are declining due to limited movement.
K9 Carts specializes in custom-built wheelchairs designed for your dog’s specific needs, ensuring a comfortable fit and optimal functionality. With our expertise, you can provide your pet with the mobility they deserve.
Caring for a Dog With Limited Mobility
Dogs with limited mobility require extra care to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life. Here are some tips:
- Preventing Pressure Sores: Use padded bedding and monitor your dog for skin irritation.
- Regular Hygiene: Clean your dog’s hindquarters to avoid infections, especially if incontinence is an issue.
- Encouraging Activity: Engage your dog in gentle exercises to maintain strength and mental stimulation.
Helping Your Dog Live a Full Life
Dragging back legs doesn’t have to mean a diminished quality of life for your dog. With the right diagnosis, treatment, and mobility aids like K9 Carts’ custom-built wheelchairs, your pet can enjoy a happy and active life.
Addressing your dog’s needs promptly is key. Consult with a trusted veterinarian, consider the benefits of tailored mobility solutions, and explore all options to ensure your dog remains comfortable and content.








